Latin American Integration Association
This article needs additional citations for verification. (August 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Latin American Integration Association Asociación Latinoamericana de Integración Associação Latino-Americana de Integração | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Administrative center | Montevideo, Uruguay |
| Working languages | |
| Type | Trade bloc |
| Membership | |
| Leaders | |
• Secretary General | Alejandro de la Peña |
| Establishment | |
• Treaty of Montevideo | 12 August 1980 |
| Area | |
• Total | 35,262,114 km2 (13,614,778 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2008 estimate | 515,722,726 |
• Density | 14.6/km2 (37.8/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC-3 to -8 |
Website http://www.aladi.org | |
The Latin American Integration Association / Asociación Latinoamericana de Integración / Associação Latino-Americana de Integração (LAIA / ALADI) is an international and regional scope organization. It was created on 12 August 1980 by the 1980 Montevideo Treaty,[1][2] replacing the Latin American Free Trade Association (LAFTA/ALALC). Currently, it has 13 member countries, and any of the Latin American States may apply for accession.
Objectives[edit]
The development of the integration process developed within the framework of the ALADI aims at promoting the harmonious and balanced socio-economic development of the region, and its long-term objective is the gradual and progressive establishment of a Latin-American Common Market.
Basic Functions[edit]
- Promotion and regulation of reciprocal trade
- Economic complementation
- Development of economic cooperation actions contributing to the markets extension.
General Principles[edit]
- Pluralism in political and economic matters;
- Progressive convergence of partial actions for the establishment of a Latin-American Common Market;
- Flexibility;
- Differential treatments based on the development level of the member countries; and
- Multiple forms of trade agreements.
Integration Mechanisms[edit]
The ALADI promotes the establishment of an area of economic preferences within the region, in order to create a Latin-American common market, through three mechanisms:
- A Regional Tariff Preference applied to goods from the member countries compared to tariffs in-force for third countries.
- Regional Scope Agreements, those in which all member countries participate.
- Partial Scope Agreements, those wherein two or more countries of the area participate.
The Relatively Less Economically Developed Countries of the region (Bolivia, Ecuador and Paraguay) benefit from a preferential system, through the lists of markets opening offered by the countries in favor of the Relatively Less Economically Developed Countries; special programs of cooperation (business rounds, pre-investment, financing, technological support); and countervailing measures in favor of the land-locked countries, the full participation of such countries in the integration process is sought. The ALADI includes in its legal structure the strongest sub-regional, plurilateral and bilateral integration agreements arising in growing numbers in the continent. As a result, the ALADI – as an institutional and legal framework or "umbrella" of the regional integration- develops actions in order to support and foster these efforts for the progressive establishment of a common economic space.
Member states[edit]
| State Members | Join Date | Population | Land Surface | Exclusive Economic Zone | Platform | Capital City |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Founder | 40,117,096 | 2,780,400 km² | 1,084,386 km² | 856,346 km² | Buenos Aires | |
| Founder | 10,426,160 | 1,098,581 km² | Landlocked | Sucre & La Paz | ||
| Founder | 190,732,694 | 8,514,877 km² | 3,660,955 km² | 774,563 km² | Brasilia | |
| Founder | 17,094,275 | 756,096.3 km² | 3,681,989 km² | 252,947 km² | Santiago de Chile | |
| Founder | 45,656,937 | 1,141,748 km² | 817,816 km² | 53,691 km² | Bogotá | |
| 1999 | 11,242,621 | 110,860 km² | 350,751 km² | 61,525 km² | Havana | |
| Founder | 14,306,876 | 283,561 km² | 1,072,533 km² | 41,034 km² | Quito | |
| Founder | 112,322,757 | 1,972,550 km² | 3,177,593 km² | 419,102 km² | Mexico City | |
| Founder | 7,030,917 | 406,752 km² | Landlocked | Asunción | ||
| 2011 | 3,405,813 | 78,200 km² | 335,646 km² | 53,404 km² | Panama City | |
| Founder | 29,885,340 | 1,285,215.6 km² | 906,454 km² | 82,000 km² | Lima | |
| Founder | 3,424,595 | 176,215 km² | 142,166 km² | 75,327 km² | Montevideo | |
| Founder | 30,102,382 | 916,445 km² | 860,000 km² | 98,500 km² | Caracas | |
| Total: | 521,213,563 | 19,651,873 km² | 16,214,170 km² | 2,839,313 km² |
Accession of other Latin American countries[edit]
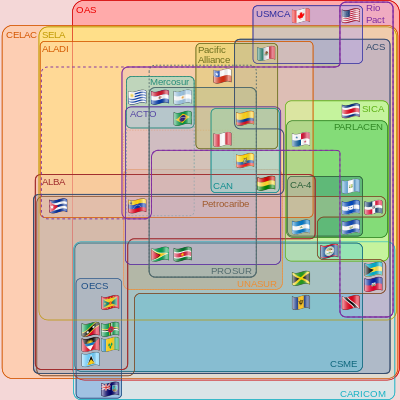
The 1980 Montevideo Treaty is open to the accession of any Latin-American country. On 26 August 1999, the first accession to the 1980 Montevideo Treaty was executed, with the incorporation of the Republic of Cuba as a member country of the ALADI. On 10 May 2012, the Republic of Panama became the thirteenth member country of the ALADI. Likewise, the accession of the Republic of Nicaragua was accepted in the Sixteenth Meeting of the Council of Ministers (Resolution 75 (XVI)), held on 11 August 2011. Currently, Nicaragua moves towards the fulfillment of conditions for becoming a member country of the ALADI. The ALADI opens its field of actions for the rest of Latin America through multilateral links or partial agreements with other countries and integration areas of the continent (Article 25). The Latin-American Integration Association also contemplates the horizontal cooperation with other integration movements in the world and partial actions with third developing countries or their respective integration areas (Article 27).
Institutional Structure[edit]
- Council of Ministers of Foreign Affairs
The Council of Ministers is the supreme body of the ALADI, and adopts the decisions for the superior political management of the integration process. It is constituted by the Ministers of Foreign Affairs of the member countries. Notwithstanding, when one of such member countries assigns the competence of the integration affairs to a different Minister or Secretary of State, the member countries may be represented, with full powers, by the respective Minister or Secretary. It is convened by the Committee of Representatives, meets and makes decisions with the presence of all the member countries.
- Evaluation and Convergence Conference
It is in charge, among others, of analyzing the functioning of the integration process in all its aspects, promoting the convergence of the partial scope agreements seeking their progressive multilateralization, and promoting greater scope actions as regards economic integration. It is made up of Plenipotentiaries of the member countries.
- Committee of Representatives
It is the permanent political body and negotiating forum of the ALADI, where all the initiatives for the fulfillment of the objectives established by the 1980 Montevideo Treaty are analyzed and agreed on. It is composed of a Permanent Representative of each member country with right to one vote and an Alternate Representative. It meets regularly every 15 days and its Resolutions are adopted by the affirmative vote of two thirds of the member countries.
- General Secretariat
It is the technical body of the ALADI, and it may propose, evaluate, study and manage for the fulfillment of the objectives of the ALADI. It is composed of technical and administrative personnel, and directed by a Secretary-General, who has the support of two Undersecretaries, elected for a three-year period, renewable for the same term.

Secretaries General[edit]
- 1980–1984
 Julio César Schupp (Paraguay)
Julio César Schupp (Paraguay) - 1984–1987
 Juan José Real (Uruguay)
Juan José Real (Uruguay) - 1987–1990
 Norberto Bertaina (Argentina)
Norberto Bertaina (Argentina) - 1990–1993
 Jorge Luis Ordóñez (Colombia)
Jorge Luis Ordóñez (Colombia) - 1993–1999
 Antônio José de Cerqueira Antunes (Brasil)
Antônio José de Cerqueira Antunes (Brasil) - 2000–2005
 Juan Francisco Rojas Penso (Venezuela) [3]
Juan Francisco Rojas Penso (Venezuela) [3] - 2005–2008
 Didier Opertti (Uruguay) [4]
Didier Opertti (Uruguay) [4] - 2008–2009
 Bernardino Hugo Saguier-Caballero (Paraguay)
Bernardino Hugo Saguier-Caballero (Paraguay) - 2009–2011
 José Félix Fernández Estigarribia (Paraguay) [5]
José Félix Fernández Estigarribia (Paraguay) [5] - 2011–2014
 Carlos Álvarez (Argentina)
Carlos Álvarez (Argentina)
See also[edit]
- Free trade
- Free trade area
- International trade
- Central America Free Trade Agreement
- Free Trade Area of the Americas
- Latin American economy
- Trade bloc
- Mercosur
- Andean Community of Nations
- Union of South American Nations
- Central American Integration System
- Caribbean Community
- Latin American Economic System
- Latin American Parliament
- PetroCaribe
References[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Latin American Integration Association. |
- ^ 1980 Montevideo Treaty (in English)
- ^ 1980 Montevideo Treaty Archived 2019-01-09 at the Wayback Machine (in Spanish)
- ^ "20th Anniversary of the Treaty of Montevideo" (in Spanish). ALADI. 2000-08-07.
- ^ "25th Anniversary of the Treaty of Montevideo" (in Spanish). ALADI. 2005-08-11.
- ^ "30th Anniversary of the Treaty of Montevideo" (in Spanish). ALADI. 2010-08-19.


No comments:
Post a Comment