Baseball positions
Baseball is a bat-and-ball game played between two opposing teams who take turns batting and fielding. Within the game there are positions in which each player can play in.
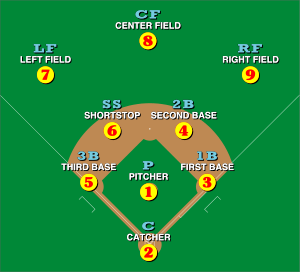
There are nine fielding positions in baseball. Each position conventionally has an associated number, for use in scorekeeping by the official scorer:
1 (pitcher), 2 (catcher), 3 (first baseman), 4 (second baseman), 5 (third baseman), 6 (shortstop), 7 (left fielder) also, less commonly known as left outfield, 8 (center fielder), and 9 (right fielder).[1] Collectively, these positions are usually grouped into three groups: the outfield (left field, center field, and right field), the infield (first base, second base, third base, and shortstop), and the battery (pitcher and catcher). Traditionally, players within each group will often be more able to exchange positions easily (that is, a second baseman can usually play shortstop well, and a center fielder can also be expected to play right field); however the pitcher and catcher are highly specialized positions and rarely will players at other positions play there.
Other roles[edit]
Other team personnel[edit]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to |
- ^ Spatz, Lyle (2012). Historical Dictionary of Baseball. Scarecrow Press. p. 3. ISBN 9780810879546.
No comments:
Post a Comment