History of the Comoros
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of the Comoros |
 |
|
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
The history of the Comoros extends to about 1000 BC when the archipelago was first inhabited. The Comoros have been inhabited by various groups throughout this time. France colonised the islands in the 19th century, and they became independent in 1975.
Early inhabitants[edit]
The earliest inhabitants of the islands were likely people from the Swahili culture from as early as 1000 BC, small trading communities of Bantu-speakers from the coasts of East Africa.
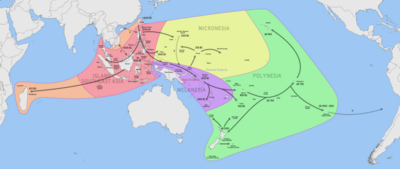
In the 8th to 13th centuries AD they were followed by an influx of Austronesian sailors from Southeast Asia, who had earlier settled nearby Madagascar. They are the source for the earliest archeological evidence of farming in the islands. Crops from archeological sites in Sima are predominantly rice strains of both indica and japonica varieties from Southeast Asia, as well as various other Asian crops like mung bean and cotton. Only a minority of the examined crops were African-derived, like finger millet, African sorghum, and cowpea. The Comoros are believed to be the first site of contact and subsequent admixture between African and Asian populations (earlier than Madagascar). Comorians today still display at most 20% Austronesian admixture.[2][3][4]
From around the 15th century AD, Shirazi slave traders established trading ports and brought in slaves from the mainland. In the 16th century, social changes on the East African coast probably linked to the arrival of the Portuguese saw the arrival of a number of Arabs of Hadrami who established alliances with the Shirazis and founded several royal clans.
Over the centuries, the Comoros have been settled by a succession of diverse groups from the coast of Africa, the Persian Gulf, Southeast Asia and Madagascar.
Europeans[edit]

Portuguese explorers first visited the archipelago in 1505.
Apart from a visit by the French Parmentier brothers in 1529, for much of the 16th century the only Europeans to visit the islands were Portuguese. British and Dutch ships began arriving around the start of the 17th century and the island of Ndzwani soon became a major supply point on the route to the East Indies. Ndzwani was generally ruled by a single sultan, who occasionally attempted to extend his authority to Mayotte and Mwali; Ngazidja was more fragmented, on occasion being divided into as many as 12 small kingdoms.
Sir James Lancaster's voyage to the Indian Ocean in 1591 was the first attempt by the English to break into the spice trade, which was dominated by the Portuguese. Only one of his four ships made it back from the Indies on that voyage, and that one with a decimated crew of 5 men and a boy. Lancaster himself was marooned by a cyclone on the Comoros. Many of his crew were speared to death by angry islanders although Lancaster found his way home in 1594. (Dalrymple W. 2019; Bloomsbury Publishing ISBN 1635573955).
Both the British and the French turned their attention to the Comoros islands in the middle of the 19th century. The French finally acquired the islands through a cunning mixture of strategies, including the policy of "divide and conquer", chequebook politics and a serendipitous affair between a sultana and a French trader that was put to good use by the French, who kept control of the islands, quelling unrest and the occasional uprising.
William Sunley, a planter and British Consul from 1848–1866, was an influence on Anjouan.
French Comoros[edit]
Territory of Comoros Territorie du Comorien | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1886-1914 1946-1963 | |||||||||||
| Administrative center | Mayotte | ||||||||||
| Administrator-Superior | |||||||||||
• 1946 | Alain Alainou | ||||||||||
• 1960-1961 | Louis Saget | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
State of the Comoros | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1963-1975 | |||||||||||
| Capital | Moroni | ||||||||||
| Government | Autonomous State of France | ||||||||||
| High Commissioner | |||||||||||
• 1962-1963 | Yves Daruvar | ||||||||||
• 1969-1975 | Jacques Mouradin | ||||||||||
| Chief Minister | |||||||||||
• 1972-1975 | Ahmed Abdallah | ||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | KM | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
On 25 March 1841, France purchased the island of Maore — the name of the island was corrupted in French to "Mayotte" — which became a colony upon ratification on 13 June 1843.
In 1850 Sultan Selim of Johanna island seized the American whaler Maria and imprisoned her commander, Captain Moores. In response, the United States Navy launched the Johanna Expedition in February 1852 to gain the release of Moores and extract compensation. Initially, the sultan did not meet the demands, and the sloop-of-war USS Dale bombarded the island's fortifications; ultimately Selim paid US$1,000 and released Captain Moores.[5][6]
In 1886 Said Ali bin Said Omar, Sultan of Bambao, signed an agreement with the French government that allowed France to establish a protectorate over the entire island of Ngazidja (Grande Comore); protectorates were also established over Ndzwani (Anjouan), and Mwali (Mohéli island in French) the same year. Résidents were posted on the three islands.
On 9 April 1908, France declared the protectorates and Mayotte a single colony, Mayotte and dependencies.
On 25 July 1912, it was annexed to Madagascar as a province of that colony.
From 16 June 1940 to 1942 the colonial administration remained loyal to Vichy France (from 1942, under Free French), but 25 September 1942 to 13 October 1946 they were, like Madagascar, under British occupation.
Until the opening of the Suez Canal, the islands used to be an important refuelling and provisioning station for ships from Europe to the Indian Ocean.
Independence came gradually for the Comoros. During the middle of the 20th century the French reluctantly began to accede to requests for constitutional changes and in 1946 the Comoros had become a separately administered colony from Madagascar.
After World War II, the islands became a French overseas territory and were represented in France's National Assembly. Internal political autonomy was granted in 1961. Agreement was reached with France in 1973 for the Comoros to become independent in 1978. On July 6, 1975, however, the Comorian parliament passed a resolution declaring unilateral independence. The deputies of Mayotte abstained.
In 1961 the Comoros was granted autonomous rule and, in 1975, it broke all ties with France and established itself as an independent republic. From the very beginning Mayotte refused to join the new republic and aligned itself even more firmly to the French Republic, but the other islands remained committed to independence. The first president of the Comoros, Ahmed Abdallah Abderemane, did not last long before being ousted in a coup d'état by Ali Soilih, an atheist with an Islamic background.
Soilih began with a set of solid socialist ideals designed to modernize the country. However, the regime faced problems. A French mercenary by the name of Bob Denard, arrived in the Comoros at dawn on 13 May 1978, and removed Soilih from power. Solih was shot and killed during the coup. Abdallah returned to govern the country and the mercenaries were given key positions in government.
In two referendums, in December 1974 and February 1976, the population of Mayotte voted against independence from France (by 63.8% and 99.4% respectively). Mayotte thus remains under French administration, and the Comorian Government has effective control over only Grande Comore, Anjouan, and Mohéli.
Later, French settlers, French-owned companies, and Arab merchants established a plantation-based economy that now uses about one-third of the land for export crops.
Abdallah regime[edit]
Federal Islamic Republic of the Comoros | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1978-2001 | |||||||||
Anthem: Comoros National Anthem | |||||||||
| Status | Islamic Republic | ||||||||
| Capital | Moroni | ||||||||
| Official languages | French, Comorian,Arabic | ||||||||
| Religion | Islam | ||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Comorian | ||||||||
| President | |||||||||
• 1978-1989 | Ahmed Abdallah | ||||||||
• 1999-2001 | Azali Assoumani | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In 1978, president Ali Soilih, who had a firm anti-French line, was killed and Ahmed Abdallah came to power. Under the reign of Abdallah, Denard was commander of the Presidential Guard (PG) and de facto ruler of the country. He was trained, supported and funded by the white regimes in South Africa (SA) and Rhodesia (now Zimbabwe) in return for permission to set up a secret listening post on the islands. South-African agents kept an ear on the important ANC bases in Lusaka and Dar es Salaam and watched the war in Mozambique, in which SA played an active role. The Comoros were also used for the evasion of arms sanctions.
When in 1981 François Mitterrand was elected president Denard lost the support of the French intelligence service, but he managed to strengthen the link between SA and the Comoros. Besides the military, Denard established his own company SOGECOM, for both the security and construction, and seemed to profit by the arrangement. Between 1985 and 1987 the relationship of the PG with the local Comorians became worse.
At the end of the 1980s the South Africans did not wish to continue to support the mercenary regime and France was in agreement. Also President Abdallah wanted the mercenaries to leave. Their response was a (third) coup resulting in the death of President Abdallah, in which Denard and his men were probably involved. South Africa and the French government subsequently forced Denard and his mercenaries to leave the islands in 1989.
1989-1996[edit]
Said Mohamed Djohar became president. His time in office was turbulent, including an impeachment attempt in 1991 and a coup attempt in 1992.
On September 28, 1995 Bob Denard and a group of mercenaries took over the Comoros islands in a coup (named operation Kaskari by the mercenaries) against President Djohar. France immediately severely denounced the coup, and backed by the 1978 defense agreement with the Comoros, President Jacques Chirac ordered his special forces to retake the island. Bob Denard began to take measures to stop the coming invasion. A new presidential guard was created. Strong points armed with heavy machine guns were set up around the island, particularly around the island's two airports.
On October 3, 1995, 11 p.m., the French deployed 600 men against a force of 33 mercenaries and a 300-man dissident force. Denard however ordered his mercenaries not to fight. Within 7 hours the airports at Iconi and Hahaya and the French Embassy in Moroni were secured. By 3:00 p.m. the next day Bob Denard and his mercenaries had surrendered. This (response) operation, codenamed Azalée, was remarkable, because there were no casualties, and just in seven days, plans were drawn up and soldiers were deployed. Denard was taken to France and jailed. Prime minister Caambi El-Yachourtu became acting president until Djohar returned from exile in January, 1996. In March 1996, following presidential elections, Mohamed Taki Abdoulkarim, a member of the civilian government that Denard had tried to set up in October 1995, became president. On 23 November 1996, Ethiopian Airlines Flight 961 crashed near a beach on the island after it was hijacked and ran out of fuel killing 125 people and leaving 50 survivors.
Secession of Anjouan and Mohéli[edit]
In 1997, the islands of Anjouan and Mohéli declared their independence from the Comoros. A subsequent attempt by the government to re-establish control over the rebellious islands by force failed, and presently the African Union is brokering negotiations to effect a reconciliation. This process is largely complete, at least in theory. According to some sources, Mohéli did return to government control in 1998. In 1999, Anjouan had internal conflicts and on August 1 of that year, the 80-year-old first president Foundi Abdallah Ibrahim resigned, transferring power to a national coordinator, Said Abeid. The government was overthrown in a coup by army and navy officers on August 9, 2001. Mohamed Bacar soon rose to leadership of the junta that took over and by the end of the month he was the leader of the country. Despite two coup attempts in the following three months, including one by Abeid, Bacar's government remained in power, and was apparently more willing to negotiate with the Comoros. Presidential elections were held for all of the Comoros in 2002, and presidents have been chosen for all three islands as well, which have become a confederation. Most notably, Mohammed Bacar was elected for a 5-year term as president of Anjouan. Grande Comore had experienced troubles of its own in the late 1990s, when President Taki died on November 6, 1998. Colonel Azali Assoumani became president following a military coup in 1999. There have been several coup attempts since, but he gained firm control of the country after stepping down temporarily and winning a presidential election in 2002.
In May 2006, Ahmed Abdallah Sambi was elected from the island of Anjouan to be the president of the Union of the Comoros. He is a well-respected Sunni cleric who studied in the Sudan, Iran and Saudi Arabia. He is respectfully called "Ayatollah" by his supporters but is considered, and is, a moderate Islamist. He has been quoted as stating that the Comoros is not ready to become an Islamic state, nor shall the veil be forced upon any women in the Comoros.[7]
2007-2008 Anjouan crisis[edit]
See also[edit]
- List of heads of state of the Comoros
- List of heads of government of the Comoros
- History of Africa
- History of Southern Africa
- Politics of the Comoros
References[edit]
- ^ Chambers, Geoff (2013). "Genetics and the Origins of the Polynesians". eLS. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. doi:10.1002/9780470015902.a0020808.pub2. ISBN 978-0470016176.
- ^ Crowther, Alison; Lucas, Leilani; Helm, Richard; Horton, Mark; Shipton, Ceri; Wright, Henry T.; Walshaw, Sarah; Pawlowicz, Matthew; Radimilahy, Chantal; Douka, Katerina; Picornell-Gelabert, Llorenç; Fuller, Dorian Q.; Boivin, Nicole L. (14 June 2016). "Ancient crops provide first archaeological signature of the westward Austronesian expansion". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 113 (24): 6635–6640. doi:10.1073/pnas.1522714113. PMC 4914162. PMID 27247383.
- ^ Brucato, Nicolas; Fernandes, Veronica; Mazières, Stéphane; Kusuma, Pradiptajati; Cox, Murray P.; Ng'ang'a, Joseph Wainaina; Omar, Mohammed; Simeone-Senelle, Marie-Claude; Frassati, Coralie; Alshamali, Farida; Fin, Bertrand; Boland, Anne; Deleuze, Jean-Francois; Stoneking, Mark; Adelaar, Alexander; Crowther, Alison; Boivin, Nicole; Pereira, Luisa; Bailly, Pascal; Chiaroni, Jacques; Ricaut, François-Xavier (January 2018). "The Comoros Show the Earliest Austronesian Gene Flow into the Swahili Corridor". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 102 (1): 58–68. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.11.011. PMC 5777450. PMID 29304377.
- ^ Msaidie, Said; Ducourneau, Axel; Boetsch, Gilles; Longepied, Guy; Papa, Kassim; Allibert, Claude; Yahaya, Ali Ahmed; Chiaroni, Jacques; Mitchell, Michael J (11 August 2010). "Genetic diversity on the Comoros Islands shows early seafaring as major determinant of human biocultural evolution in the Western Indian Ocean". European Journal of Human Genetics. 19 (1): 89–94. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2010.128. PMC 3039498. PMID 20700146.
- ^ "The Bombardment of Johanna". 4 February 1852 – via NYTimes.com.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-05-10. Retrieved 2011-04-28.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Comoros: Presidential Favourite Clear - By a Landslide". 15 May 2006 – via AllAfrica.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (October 2006) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |








No comments:
Post a Comment