Geography of Gabon
  | |
| Continent | Africa |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 1°00′N 11°45′E / 1.000°N 11.750°E |
| Area | Ranked 77th |
| • Total | 267,667 km2 (103,347 sq mi) |
| • Land | 96.3% |
| • Water | 3.7% |
| Coastline | 885 km (550 mi) |
| Highest point | Mont Bengoué, 1070 m (not Mont Iboundji as claimed by some authorities) |
| Lowest point | Atlantic Ocean, 0 m |
| Longest river | Ogooué River |
| Climate | Tropical monsoon ('Am'), Tropical savanna ('Aw'); always hot, humid |
| Terrain | narrow coastal plain; hilly interior; savanna in east and south |
| Natural resources | Petroleum, natural gas, diamond, niobium, manganese, uranium, gold, timber, iron ore, hydropower |
| Environmental issues | deforestation, poaching |
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
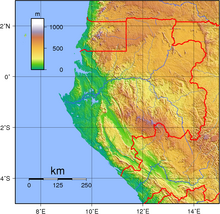
Gabon is a country in Central Africa, lying along the Atlantic Ocean, just south of the Bight of Biafra.
Borders[edit]
Gabon has a total of 3,261 km of international boundaries. It borders Equatorial Guinea (335 km) and Cameroon (349 km) to the north and the Republic of the Congo (2,567 km) to the east and south. Gabon lies on the equator.
- Maritime claims
-
- Territorial sea: 12 nmi (22 km)
- Contiguous zone: 24 nmi (44 km)
- Exclusive economic zone: 200 nmi (370 km)
Climate[edit]
Gabon has the moist, hot climate typical of tropical regions. The hottest month is January, with an average high at Libreville of 31 °C and an average low of 23 °C. Average July temperatures in the capital range between 20 and 28 °C. From June to September there is virtually no rain but high humidity; there is occasional rain in December and January. During the remaining months, rainfall is heavy. The excessive rainfall is caused by the condensation of moist air resulting from the meeting, directly off the coast, of the cold Benguela Current from the south and the warm Guinea Current from the north. At Libreville, the average annual rainfall is more than 2540 mm. Farther north on the coast, it is 3810 mm.
Terrain[edit]
| Land Use | (2012) |
|---|---|
| • Arable land | 1.26% |
| • Permanent crops | 0.66% |
| • Other | 98.08% |
Narrow coastal plain with patches of Central African mangroves; hilly interior; savanna in east and south.
- Irrigated land: 44.5 km2 (2003)
- Total renewable water resources: 164 km3 (2011)
Environment[edit]
International agreements:
Party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
Extreme points[edit]
- Northernmost point - unnamed location on the border with Cameroon on the Ntem River, Woleu-Ntem province
- Easternmost point - the unnamed location on the border with the Republic of Congo immediately south-west of the Congolese village of Mbeyi-Mbola, Haut-Ogooué province
- Southernmost point - the point at which the border with the Republic of Congo enters the Atlantic Ocean, Nyanga Province
- Westernmost point - the north-west point of Cape Lopez, Ogooué Maritime province
See also[edit]
References[edit]
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook website https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/.
This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook website https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/.



No comments:
Post a Comment