Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean
This article needs additional citations for verification. (October 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean Îles Éparses de l'océan Indien | |
|---|---|
Motto: "Liberté, égalité, fraternité" | |
Anthem: "La Marseillaise" "The Marsellaise" | |
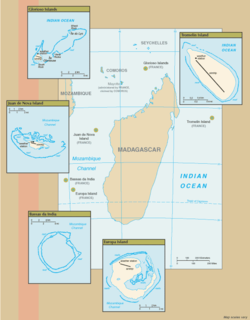 Maps of the Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean. Anti-clockwise from top right: Tromelin Island, Glorioso Islands, Juan de Nova Island, Bassas da India, Europa Island. Banc du Geyser is not shown. |
The Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean (French: Îles Éparses or Îles Éparses de l'océan Indien) consist of four small coral islands, an atoll, and a reef in the Indian Ocean, and have constituted the 5th district of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands (TAAF),[1] though sovereignty over some or all of the Islands is contested by Madagascar, Mauritius, and the Comoros. None of the islands has ever had a permanent population.
Two of the islands—Juan de Nova and Europa—and the Bassas da India atoll lie in the Mozambique Channel west of Madagascar, while a third island, Tromelin, lies about 450 kilometres (280 mi) east of Madagascar and the Glorioso Islands lies about 200 kilometres (120 mi) northwest of Madagascar. Also in the Mozambique Channel is the Banc du Geyser, a submerged reef considered a part of the Glorioso Islands by France and the Comoros.
The islands have been classified as nature reserves. Except for Bassas da India, they all support meteorological stations: those on the Glorioso Islands, Juan de Nova, and Europa Island are automated. The station on Tromelin Island, in particular, provides warning of cyclones threatening Madagascar, Réunion, or Mauritius. Each of the islands, except Bassas da India and Banc du Geyser, has an airstrip of more than 1,000 metres (3,300 ft).
Overview[edit]
| Island/Atoll | Station Staff | Area km² | Lagoon km² | EEZ km² | Coordinates | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Banc du Geyser) | 11 | 5 | 29.6 | 48,350 | 11°33′S 47°20′E / 11.550°S 47.333°E | North Mozambique Channel |
| 19 | 0.8 | – | 280,000 | 15°53′S 54°31′E / 15.883°S 54.517°E | Western Indian Ocean | |
| 14 | 4.4 | (1) | 61,050 | 17°03′S 42°45′E / 17.050°S 42.750°E | Central Mozambique Channel | |
| – | 0.2 | 79.8 | 123,700 | 21°27′S 39°45′E / 21.450°S 39.750°E | South Mozambique Channel | |
| 12 | 28 | 9 | 127,300 | 22°20′S 40°22′E / 22.333°S 40.367°E | South Mozambique Channel | |
| Total | 56 | 38.4 | 118.4 | 640,400 |
Individual islands[edit]
- Bassas da India
- Ten unnamed rock islets
- Europa Island
- Île Europa
- Eight unnamed rock islets
- Glorioso Islands
- Banc du Geyser
- Grande Glorieuse
- Île du Lys
- South Rock
- Verte Rocks (three islets)
- Wreck Rock
- Three unnamed islets
- Juan de Nova Island
- Tromelin Island
Administration[edit]
Since January 3, 2005, the Îles Éparses have been administered on behalf of the French state by the senior administrator of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands (TAAF — les Terres Australes et Antarctiques Françaises), based in Réunion. The Îles Éparses had previously been under the administration of the prefect of Réunion since the independence of Madagascar in 1960. France maintains a military garrison of around 14 troops on each of the islands in the Mozambique Channel that are claimed by Madagascar. The Glorioso Islands are also claimed by the Comoros, while Mauritius claims Tromelin Island.
France has an exclusive economic zone (EEZ) of 200 nautical miles (370 km) around each of the small islands in the Îles Éparses, which together with the EEZ claims for the islands of Réunion and Mayotte totals more than one million square kilometres (400,000 sq mi) in the western Indian Ocean. There is considerable overlap of the EEZ with the neighbouring states.
Sovereignty dispute[edit]
Mauritius, Madagascar, and the Comoros dispute France's sovereignty over these islands. Mauritius claims Tromelin and states that the island, discovered by France in 1722, was not ceded by the Treaty of Paris in 1814. Madagascar claims sovereignty over the Glorioso Islands (including Banc du Geyser), though the islands were never a part of the Malagasy Protectorate, having been a part of the Colony of Mayotte and dependencies, then a part of the French Comoros that had become a separately administered colony from Madagascar in 1946. The Comoros also claims the Glorioso Islands (including Banc du Geyser), as a part of the disputed French region of Mayotte. Furthermore, Madagascar has also claimed Juan de Nova, Europa, and Bassas da India since 1972,[2] and a 1979 United Nations resolution (without binding force) demanded the cession of these islands to Madagascar.[3][4] Seychelles claimed a part of the Scattered Islands too before the signing of the France–Seychelles Maritime Boundary Agreement.
See also[edit]
- Administrative divisions of France
- French Southern and Antarctic Lands
- List of territorial disputes
- Overseas France
References[edit]
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2010-01-28. Retrieved 2010-02-20.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) French Southern and Antarctic Lands (TAAF) Official website
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-10-30. Retrieved 2009-08-17.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "United Nations Resolution 34/91" [Question of the Islands of Gloriesus, Juan de Nova, Europa and Bassas da India]. United Nations. 12 December 1979. Retrieved 13 June 2020.
- ^ "United Nations Resolution 35/123" [Question of the Islands of Gloriesus, Juan de Nova, Europa and Bassas da India]. United Nations. 11 December 1980. Retrieved 13 June 2020.
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean. |
- 2007 establishments in Africa
- 2007 establishments in France
- Dependent territories in Africa
- Disputed islands
- French Southern and Antarctic Lands
- Islands of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands
- Island countries of the Indian Ocean
- Islands of Africa
- Islands of Madagascar
- Mozambique Channel
- Protected areas of Africa
- Protected areas of Overseas France
- Southeast African countries
- States and territories established in 2007
- Uninhabited islands of France
- Irredentism


No comments:
Post a Comment