Aliphatic compound


In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons (compounds composed solely of carbon and hydrogen) are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds (/ˌælɪˈfætɪk/; G. aleiphar, fat, oil), also known as non-aromatic hydrocarbons. Aliphatics can be cyclic; however, hydrocarbons with conjugated pi-systems that obey Hückel's rule are instead considered to be aromatic.[1] Aliphatic compounds can be saturated, like hexane, or unsaturated, like hexene and hexyne. Open-chain compounds (whether straight or branched) contain no rings of any type, and are thus aliphatic.
Structure[edit]
Aliphatic compounds can be saturated, joined by single bonds (alkanes), or unsaturated, with double bonds (alkenes) or triple bonds (alkynes). Besides hydrogen, other elements can be bound to the carbon chain, the most common being oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, and chlorine.
The least complex aliphatic compound is methane (CH4),ethane(c2h6)
Properties[edit]
Most aliphatic compounds are flammable, allowing the use of hydrocarbons as fuel, such as methane in Bunsen burners and as liquefied natural gas (LNG), and ethyne (acetylene) in welding.
Examples of aliphatic compounds / non-aromatic[edit]
The most important aliphatic compounds are:
- n-, iso- and cyclo-alkanes (saturated hydrocarbons)
- n-, iso- and cyclo-alkenes and -alkynes (unsaturated hydrocarbons).
Important examples of low-molecular aliphatic compounds can be found in the list below (sorted by the number of carbon-atoms):
| Formula | Name | Structural Formula | Chemical Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | Methane | 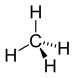 | Alkane |
| C2H2 | Acetylene | Alkyne | |
| C2H4 | Ethylene |  | Alkene |
| C2H6 | Ethane |  | Alkane |
| C3H4 | Propyne | Alkyne | |
| C3H6 | Propene | 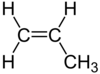 | Alkene |
| C3H8 | Propane |  | Alkane |
| C4H6 | 1,2-Butadiene |  | Diene |
| C4H6 | 1-Butyne |  | Alkyne |
| C4H8 | 1-Butene | Alkene | |
| C4H10 | Butane | 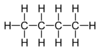 | Alkane |
| C6H10 | Cyclohexene | Cycloalkene | |
| C5H12 | n-pentane | Alkane | |
| C7H14 | Cycloheptane | Cycloalkane | |
| C7H14 | Methylcyclohexane | 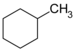 | Cyclohexane |
| C8H8 | Cubane |  | Octane |
| C9H20 | Nonane | Alkane | |
| C10H12 | Dicyclopentadiene |  | Diene, Cycloalkene |
| C10H16 | Phellandrene |   | Terpene, Diene Cycloalkene |
| C10H16 | α-Terpinene | Terpene, Cycloalkene, Diene | |
| C10H16 | Limonene |  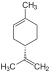 | Terpene, Diene, Cycloalkene |
| C11H24 | Undecane | Alkane | |
| C30H50 | Squalene | Terpene, Polyene | |
| C2nH4n | Polyethylene |  | Alkane |
References[edit]
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (1995) "aliphatic compounds". doi:10.1351/goldbook.A00217
No comments:
Post a Comment